If you're an employee of an eligible firm, a 401kis a tax-deferred savings plan that you can save and invest for your own retirement. An employee's 401kplan can only be sponsored by their company. According to plan and IRS regulations, you determine how much money you want to take out of your paycheck and place into your 401(k). Contributions from your employer are a possibility, but it is not required.

What Is a 401(k)?
401(k)s are employer-sponsored defined-contribution plans (DC) that allow workers to save for retirement in a tax-advantaged manner. You can allocate a percentage of your income to a 401(k)planoffered by your employer. You can minus the donations from your taxes because they are automatically deducted from your salary.
How does a 401k work?
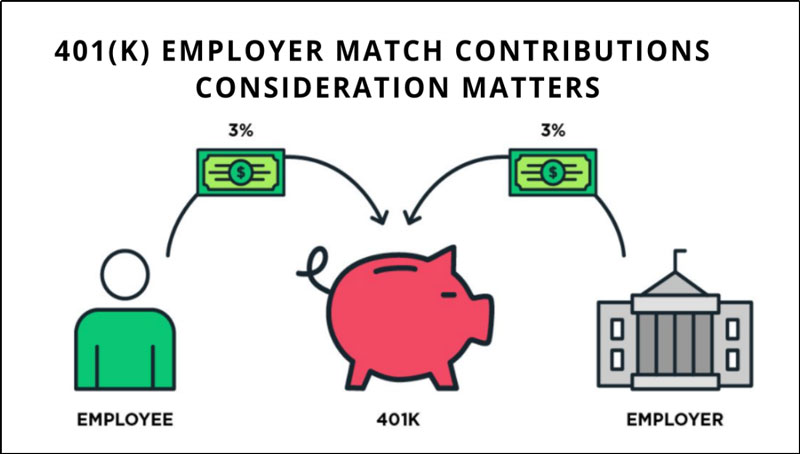
Employers frequently provide their workers with a 401k planas a means of ensuring that they will have enough money set aside for their golden years. Every time an employee receives a paycheck, a certain percentage is deducted and automatically invested in a 401(k) plan. Typically, they are made up of investments (stocks, bonds, mutual funds) that the employee has the option of selecting.
Employer matching contributions and tax-free investments may be available depending on the plan's specifics. Financial experts recommend that you contribute the maximum amount possible to your 401k planeach year, or as near to it as you can afford.
Types of 401(K) Plans:
Here are the different types of 401(k) plans you can have at your business:
- Traditional 401(k) plans
- Safe harbor 401(k) plans
- SIMPLE 401(k) plans
- Solo 401(k) plans
- Roth 401(k) plans
Retirement plansare often able to be coupled with other plans. When it comes to 401(k) plans, there are both standard and Roth options.
Set rules for contributions, such as a waiting time, if you contribute to a 401(k) planas an employer. Employees may have to work for you for six months before they are eligible to make a financial contribution.
In terms of flexibility, contribution limitations, and business size, each option for establishing a 401(k) planfor a small business is distinct from the others in this category. You should compare the various 401(k)options before making a selection for your organization.

Traditional 401(K):
Traditional 401(k) plansare popular among organizations looking to provide retirement benefits to their employees. As an employer-sponsored retirement plan, it also provides employees with a wide range of investing possibilities. Traditional 401(k)contributions and investment gains are tax-deferred. Savings are exempt from income tax until they are withdrawn. Some firms match a percentage of their employees' 401(k)contributions in order to provide the benefit to their employees. Employer matching payments are taxed only when the savings are withdrawn, deferring the tax until the savings are withdrawn.
SIMPLE 401(K):
SIMPLE 401(k) plansare perfect for small business owners or self-employed professionals with less than 100 workers. A simplified form of a standard 401(k)plan, this type of plan is offered. It is possible to combine the simplicity of a SIMPLE IRA with the functionality of an ordinary 401(k) plan. Nondiscrimination tests aren't required with a SIMPLE 401(k). Once you make a contribution to a SIMPLE 401(k), it is non-refundable. Because of this, employees who participate in a SIMPLE 401(k)plan are not eligible to receive contributions or accruals from any other employer-sponsored retirement plan.
Safe Harbor 401(K):
To qualify for the non-discrimination test, 401(k) retirement plansmust include a Safe Harbor strategy. Companies are required to contribute to their employees' 401(k) plansunder this unique structure. A "safe harbor" from both the non-discrimination test and the penalty of failure is given to firms who take this measure to boost employee involvement.
Solo 401(K):
Only one person can participate in a solo 401(k) plan. There are no employees other than the business owner or self-employed individual and their spouse or business partners in this 401(k) plan. These plans are also known as solo 401(k)s and as self-employed 401(k)s. For employees and employers alike, the plan provides a way to contribute to retirementsavings. Owners of small businesses can benefit from this by maximizing their retirementcontributions and business tax deductions. You can deduct all of your contributions from your taxes.
Roth 401(K):
An employer-sponsored Roth 401(k) planis comparable to a standard 401(k) plan, but for one important difference: It allows employees to contribute to their retirementaccounts tax-free. It's important to note that Roth donations are not tax-deferred, but rather are made with post-tax money. Interest, capital gains, and dividends received from a Roth account are tax-free. People who expect to be in a higher tax bracket when they retire should opt for a Roth 401(k). This Roth account can also assist younger workers and higher-earning individuals. It's a win-win situation for everyone.